Understanding the Sales Pipeline dives deep into the world of sales strategies, offering a comprehensive guide that guarantees success in the competitive business realm.
Learn how to navigate the intricate stages of a sales pipeline and unlock the secrets to boosting revenue like never before.
What is a Sales Pipeline?
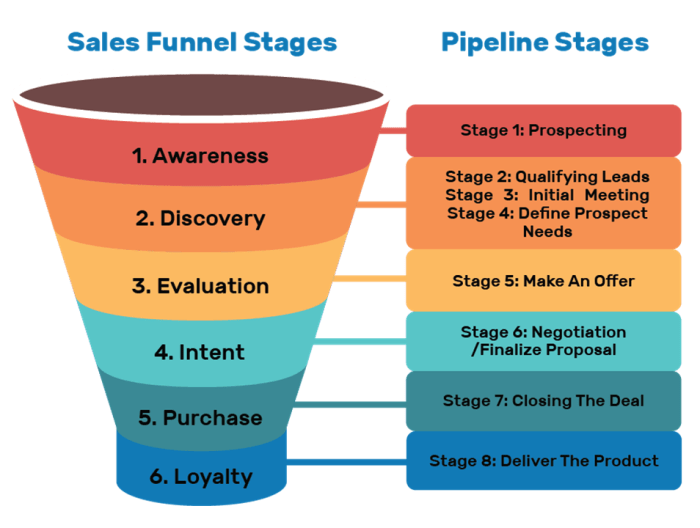
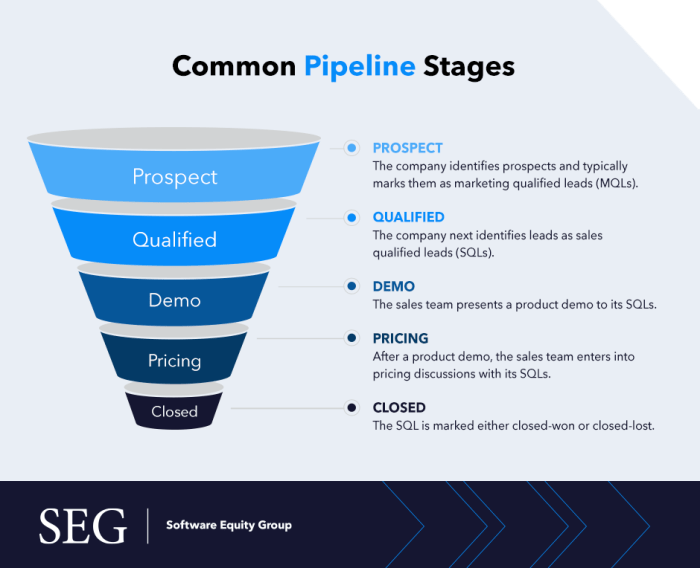
A sales pipeline is a visual representation of the stages a customer goes through before making a purchase. It helps businesses track and manage the sales process from lead generation to closing the deal.
Stages in a Typical Sales Pipeline
- Lead Generation: This is where potential customers are identified and initial contact is made.
- Qualification: Leads are assessed to determine their likelihood of converting into customers.
- Proposal: Sales reps present a solution or offer to the qualified leads.
- Negotiation: Discussions on terms, pricing, and finalizing the deal take place.
- Closing: The customer commits to making a purchase and the deal is closed.
Industries Using Sales Pipelines, Understanding the Sales Pipeline
Sales pipelines are commonly used in industries such as:
- Real Estate: Agents use pipelines to track leads and manage property transactions.
- Tech: Software companies use pipelines to sell their products and services to businesses.
- Retail: Stores use pipelines to manage customer interactions and drive sales.
Importance of Understanding the Sales Pipeline
Businesses need to understand their sales pipeline to effectively manage and track their sales process. By having a clear view of where each lead is in the pipeline, companies can make informed decisions, allocate resources appropriately, and forecast sales more accurately.
Increased Revenue Potential
A well-managed sales pipeline can lead to increased revenue by optimizing the sales process. When sales teams have a clear understanding of the pipeline, they can identify bottlenecks, prioritize high-value leads, and focus on activities that are most likely to result in closed deals. This targeted approach can significantly boost sales and revenue generation.
Benefits for Sales Teams
- Improved Efficiency: Sales teams can streamline their activities and focus on leads that are more likely to convert, leading to higher productivity.
- Better Forecasting: With a clear view of the pipeline, sales teams can accurately predict future revenue and set realistic targets.
- Enhanced Communication: Understanding the sales pipeline helps sales teams collaborate more effectively, share insights, and support each other in closing deals.
- Customer Relationship Management: By tracking leads through the pipeline, sales teams can provide personalized and timely communication to nurture relationships and increase customer satisfaction.
Designing an Effective Sales Pipeline: Understanding The Sales Pipeline
To create a successful sales pipeline, it is crucial to pay attention to key elements that will help streamline the process and drive sales. By comparing different approaches and implementing best practices, you can optimize the design of your sales pipeline for maximum efficiency.
Key Elements of Designing a Successful Sales Pipeline
- Define Stages: Clearly Artikel the different stages that a lead goes through in the sales process, from initial contact to closing the deal.
- Set Clear Criteria: Establish specific criteria for advancing leads from one stage to the next, ensuring consistency and transparency.
- Automate Processes: Utilize technology and automation tools to streamline tasks, track progress, and improve communication within the pipeline.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly analyze and evaluate the performance of the pipeline to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
Different Approaches to Structuring a Sales Pipeline
- Linear Approach: In a linear pipeline, leads move sequentially from one stage to the next, following a predetermined path.
- Parallel Approach: In a parallel pipeline, leads can advance through multiple stages simultaneously, allowing for more flexibility and customization.
- Hybrid Approach: Combining elements of both linear and parallel structures to create a hybrid pipeline that meets the specific needs of the business.
Best Practices for Optimizing Sales Pipeline Design
- Regularly Review and Update: Continuously review and update the pipeline design to adapt to changing market conditions and customer needs.
- Align Sales and Marketing: Ensure alignment between sales and marketing teams to facilitate a smooth transition of leads through the pipeline.
- Provide Training and Support: Offer training and support to sales reps to ensure they understand the pipeline structure and can effectively navigate it.
- Utilize Data Analytics: Leverage data analytics to gain insights into pipeline performance and make data-driven decisions for improvement.
Tools and Technologies for Managing Sales Pipelines
In today’s fast-paced business environment, having the right tools and technologies to manage sales pipelines is crucial for success. These tools help sales teams stay organized, track progress, and ultimately close deals more efficiently.
CRM Systems Streamlining the Sales Pipeline Process
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems play a vital role in streamlining the sales pipeline process. These platforms allow sales teams to store customer information, track interactions, and manage leads all in one place. By utilizing a CRM system, sales reps can easily prioritize leads, follow up with prospects, and monitor their progress through the sales pipeline.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sales Pipeline Management Tools
- CRM Software: CRM software offers a centralized platform for managing customer relationships, sales activities, and pipeline progress. It provides valuable insights into customer behavior and helps sales teams make data-driven decisions. However, some CRM systems can be complex to set up and maintain, requiring training for users.
- Sales Force Automation (SFA) Tools: SFA tools automate repetitive sales tasks, such as data entry, lead scoring, and email follow-ups. These tools help sales reps save time and focus on building relationships with prospects. On the downside, SFA tools may lack the customization options available in CRM systems.
- Pipeline Analytics Platforms: Pipeline analytics platforms offer in-depth insights into pipeline performance, conversion rates, and sales forecasting. These tools help sales managers identify bottlenecks in the pipeline and optimize their sales strategy. However, some platforms may require integrations with other tools for full functionality.